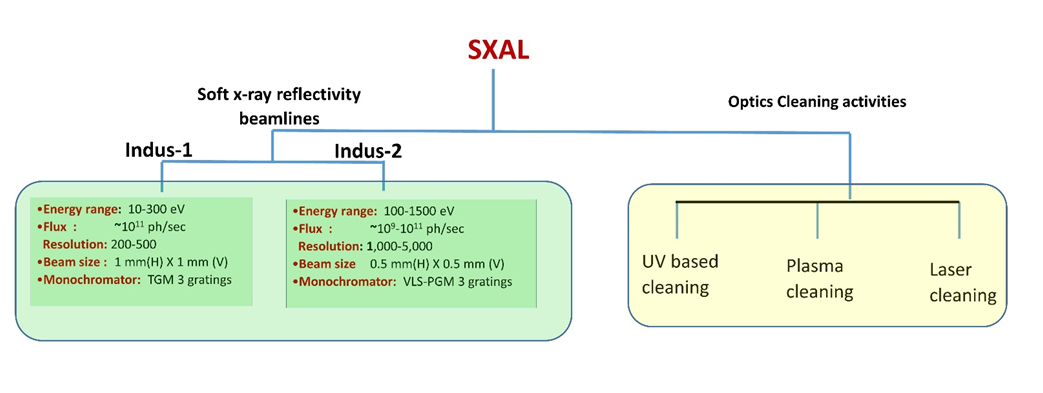
The SXAL is looking after two beamlines of soft x-ray reflectivity techniques installed on Indus-1 (BL-04) and Indus-2 (BL-03). The lab provides support to the users of soft x-ray reflectivity experiments for reflectivity, absorption and transmission measurements in the photon energy range of 10-300 eV and 100- 1500 eV. Besides that the lab is engaged in development of in-house technology for refurbishing x-ray optical components by removing carbon contamination layer from the optics surface. In synchrotron environment a carbon contamination layer grows on optical surfaces which deteriorates the optics performances, resultantly the optics needs to be refurbished. The lab is involved in various research activities also pertaining to soft x-ray reflectivity, and soft x-ray absorption properties of various materials.
Major Activities
- Support beamline users on Indus-1 and Indus-2 soft x-ray reflectivity beamlines.
- Design and development of synchrotron optics refurbishing technology.
- Studies on plasma/laser/ and UV interaction with different allotropes of carbon in perspective of synchrotron optics cleaning.
- Studies on soft x-ray optical behavior of various oxides, carbides and compound materials. Role of core hole and core exciton in soft x-ray optical properties of various materials.
- Soft x-ray resonant reflectivity for nondestructive structural and compositional analysis.
Synchrotron optic cleaning activity
Carbon contamination is a serious problem in synchrotron beamlines, mainly because it decreases the beam throughput and deteriorates the data quality. Interaction of intense synchrotron beam with the residual hydrocarbon molecules lead to the formation of carbon contamination layer. This contamination layer gradually thickens and gold or platinum coated optical elements become dark blackish in color. The contaminated optical elements need to be replaced or refurbished to maintain the beamline performance. In order to remove the contamination layer from the optics surfaces, an optics cleaning facility is developed. Depending on the types of contamination and optics size following three differ techniques are used.
A capacitive coupled radio frequency plasma system is in-house developed for cleaning the x-ray mirrors upto one meter in length. The system is equipped with a mass flow controller, a 600 watt, a 13.56 MHz frequency rf source, and a dynamic vacuum pumping system. The RF plasma system is shown in figure.
|
|
(a) RF plasma cleaning system for cleaning one meter long optics |
(b) Internal view of plasma system with oxygen gas plasma |
|
Photograph of Au coated spherical mirror of soft x-ray reflectivity beamline BL-03, Indus-2 taken before (left) and after (right) RF plasma cleaning. |
A Xenon UV source of 172 nm wavelength is available to clean the small size optics ( < 150 mm in length). The system radiates UV radiation with intensity of 50 mWatt/cm2. The synchrotron optics cleaned with UV source is shown in figure.
Photograph of Au coated spherical mirror of ARPES beamline BL-10, Indus-2 taken before (left) and after (right) RF plasma cleaning.
Photographs of spherical grating of Photophysics beamline BL-05, Indus-1 taken (left) before and (right) after UV cleaning experiments
In laser based carbon cleaning system a 1064 nm fiber laser precisely scans on the carbon contaminated region of optics surface. The carbon from the optics surface is removed by thermal ablation mechanism. In single scan the lase system can scan 150 * 150 mm2 area and in multiple scan setting it can scan large area. The scheme of laser scan is shown in figure.
Laser scan scheme for optics cleaning
Team Members
- Dr. Mohammed H. Modi, SO/H
- Shri Praveen Kumar Yadav, SO/F
- Shri Rajkumar Gupta, SO/D
- Shri Pushkardeep, SA/C
|














